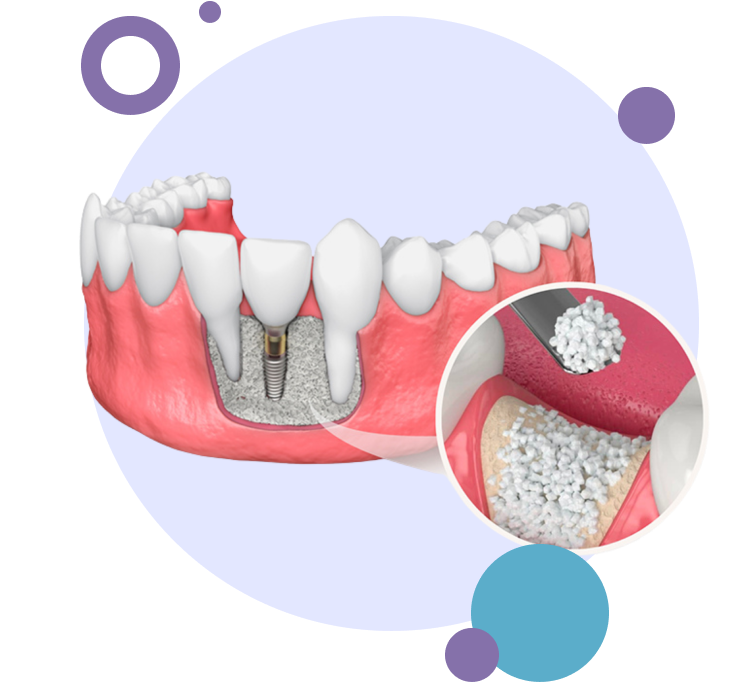
Why might I need to have bone grafts?
Bone grafting is a highly successful procedure in most cases. It is also a preferable alternative to having missing teeth, diseased teeth, or tooth deformities. Bone grafting can increase the height or width of the jawbone and fill in voids and defects in the bone.
There are essentially two basic ways in which bone grafting can positively impact the health and stability of the teeth:
Jaw Stabilization – Bone grafting stabilizes and helps restore the jaw foundation for restorative or implant surgery. Deformities can also be corrected and the restructuring of the bone can provide added support.
Preservation – Bone grafting can be used to limit or prevent bone recession following a
tooth extraction, periodontal disease, or other invasive processes.
What Does Bone Grafting Involve?
Oral Examination
Initially, Dr. Souliman will thoroughly examine the affected area in order to assess the general condition of the teeth and gums. If periodontal disease is present or the adjacent teeth are in poor condition, these factors will be fully addressed before the bone grafting procedure can begin. Dr. Souliman will also recommend
panoramic x-rays in order to assess the precise depth and width of the existing bone. On occasion, a
CT scan may be recommended to determine the bone condition. Depending on these results, it may be necessary to anesthetize the area and explore into the gum in order to determine what kind and how much bone is required.
There are several types of bone grafts. Dr. Souliman will determine the best type for your particular condition.
Autogenous Bone Graft - Harvested from the patient’s own body (usually from the posterior part of the lower jaw or the chin). This method is usually preferred because it produces the most predictable results.
Allograft Bone Graft - Cadaver or synthetic bone is used in this type of graft.
Xenograft - Cow bone is used in this type of graft.
The bone grafting procedure can often take several months to complete. This grafted bone material will fuse with the existing bone and the migration of cells will cause firm adhesion and cell growth. Supplementing the jaw with bone will result in greater bone mass to help support and anchor the
implant(s) or other dental appliance.
During the surgery, the grafting site (and extraction site if using a patient's own bone for the graft) will be numbed using local anesthetic. A small incision will be made to prepare the site for the new bone material and it will be anchored into place. On occasion, a synthetic membrane may be used to cover the new bone. This membrane prevents soft tissue and bacterial invasions, and encourages new bone growth. The surgery does not require an overnight stay, and you will be provided with comprehensive instructions for your post-operative care. Medications will be prescribed to help manage infection, discomfort and swelling.